what native plant is taking over parts of the everglades due to excess nutrients

We all think about the nutrition nosotros need in our own diets, time and fourth dimension again. At least, I certainly hope that the majority of you out there practise!
Are you getting enough atomic number 26? How well-nigh protein? Vitamins and other minerals?
Well, these very same questions can be posed to your plants. After all, your lawn and garden companions are living things like you and me, needing nutrition and sustenance to survive.
No surprise, right? Every good gardener knows to fertilize their garden denizens with well-balanced applications and establish food and compost when they need it.

We link to vendors to help you find relevant products. If you buy from ane of our links, we may earn a commission .
However, experienced gardeners – and farmers, too – learn the exact nutrients needed at any stage of growth, for health, beauty, and even tastiness. Further, they can pick upward on what plants need through various signs and indicators, diagnosing illnesses, pest issues, and food deficiencies.
The good news? You lot don't take to be a rocket scientist, an expert farmer, or even a gardener to learn these signs, and what they indicate.
All you need to do is learn a few elementary tricks and tips about found food – which we will delve into correct here in this article!
What You'll Acquire
- Plants Need Nutrition, Too
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Feeding Your Plants a Counterbalanced Nutrition
- N-P-Chiliad Explained
- Different Ratios
- Specialized Ratios
- Types of Fertilizers and Soil Amendments
- Synthetic or Chemic
- Organic
- Natural Amendments
- Compost
- Mulch
- Wood Ash
- Lime
- Gypsum
- A Fourth dimension and Place for Nutrients
- Appearance and Color
- Plant Growth Stages
- Using Nutrients to Foreclose Establish Problems
- Fungal Plant Diseases
- Viral Plant Diseases
- Bacterial Plant Diseases
- Pests
- Amendments Tin can Affect Soil Weather
Plants Need Nutrition, Also
.Experienced gardeners – and farmers, as well – learn the verbal nutrients needed at any stage of growth, for health, beauty, and even tastiness. Farther, they can choice upwards on what plants need through various signs and indicators, diagnosing illnesses, pest issues, and nutrient deficiencies.

So, what do our garden companions demand to consume, and how can you provide that for them?
More importantly – what nutrients are you supposed to be paying attention to in your fertilizers? What practise your plants really need?
As it turns out, some of them are the same ones that animals (including humans) demand. Let'due south take a look:
Nitrogen (North)
Achieves similar benefits as protein in animals (in fact, protein releases nitrogen for employ in humans). Vital for good stalk growth, though backlog decreases amnesty and power to fruit.
Phosphorus (P)
Strengthens root systems, capacity for seed creation, illness resistance, and pest prevention. Improves flowers and blooming. Also strengthens tissues and flavors in edibles and veggies.
Potassium (K)
Also important for roots and seed production. Sometimes chosen potash, this farther supports the ability to tolerate extreme temperatures. Excess prevents absorption of other minerals, particularly magnesium and calcium.
Calcium
Strengthens and fortifies overall tissues everywhere. As well helps neutralize acerbity, both within the plant and in its surrounding soil, for optimal health.
Magnesium
Helps increase intake of phosphorus and boosts production of chlorophyll, giving a healthy green color and encouraging absorption of CO2. A lack of magnesium can contribute to poor coloring and an anemic appearance.
While plants need all of these nutrients (and a scattering more through other trace minerals) for optimal health, higher numbers of some are more necessary at some times than others.
Why would that be?
Feeding Your Plants a Counterbalanced Diet
I'm sure that these minerals audio more than familiar. That'south considering they are essential to the human diet, too!
Like the states, our garden buddies need diet in the right amounts from diverse sources. Calculating the required quantity of nutrients is very necessary, as is because the correct manner to provide information technology.

Just like in that location are many foods you should include in your diet, an array of fertilizers and amendments may be needed in varying amounts to give your veggies, shrubs, and trees their own skillful "nutrition" – and a balance of these nutrients is crucial.
To deliver this full range to your garden friends, you can purchase dissimilar fertilizers with contrasted levels and types of nutrients.
At the top of our list in terms of convenience, the majority of fertilizers y'all buy accept a set, good for you residue of these nutrients built right in – particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, labeled as an "North-P-K" ratio on packaging, and fabricated up of three numbers. These three minerals brand upwards the virtually important micronutrients that most species and varieties in your garden need.
When considering feeding, ratio numbers on the packaging may vary, depending on their specific blends:
N-P-K Explained
The N-P-K amount of nearly foods will accept three identical numbers – such as 6-half dozen-6, indicating a fertilizer containing 6% each of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus for general nutrition (and maybe a whiff of sulphur…?).
Different Ratios
Other mutual kinds tend to have a higher ratio of nitrogen compared to the remainder, such as 20-6-6. This is because plants typically demand more than nitrogen than other nutrients – just like humans need more poly peptide (a macronutrient), versus other vitamins and minerals (micronutrients).
Specialized Ratios
Otherwise, you can seek formulas that focus on specific needs, rather than general intendance. For instance, a great formula for good rooting and post-transplanting care would be 6-20-20, having high P and G levels; for good flowering, await for 6-xx-6, with college quantities of phosphorus to back up and protect bloom evolution.
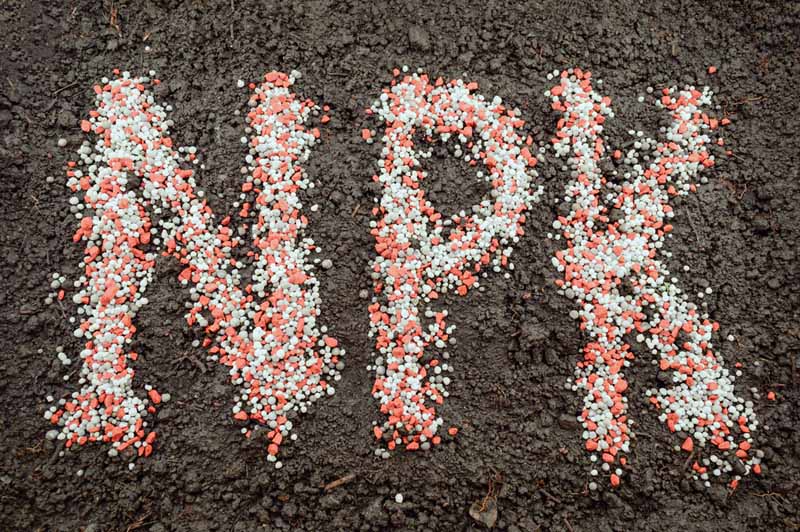
With these particularities in mind, you'll want to make sure you're using the right fertilizer for your specific needs – bringing us to the colorful array of plant foods out in that location from which to choose!
Types of Fertilizers and Soil Amendments
Like to the importance of a healthy diet in your own daily life, each inhabitant of your garden volition need to exist fed a variety of foods and fertilizers that are nutrient rich in lodge to stay strong and thriving.
The nearly of import difference here is that, while most of us tin become upwardly and become when our stomachs rumble and information technology'southward time to hit the kitchen or pay a visit to our favorite restaurant, plants are mostly immobile, rooted to the ground that doubles equally their feeding source.
Without the proper nutrients literally in place, and because our plant friends lack the ability to head out to the grocery store once a week, we demand to provide the nutrients required to come across their needs.
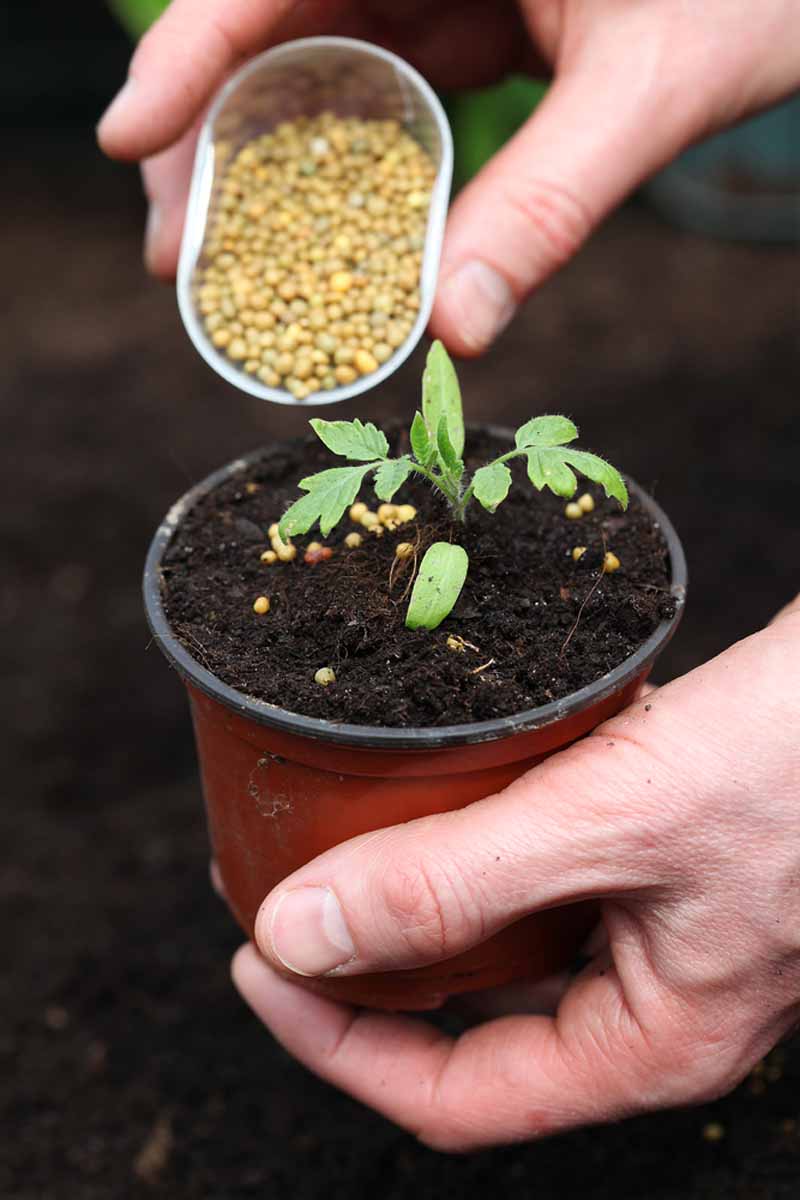

These tin can come in the course of synthetic, pre-packaged, and often chemic fertilizers that provide these nutrients for immediate, available use.
For the more eco-conscious gardener, still, at that place are also all-natural, organic, pre-packaged alternatives – as well every bit an entire earth of natural materials, composts, and mulches that are ripe for the taking.
They may not human activity or provide nutrition every bit fast or equally intensely as commercially made fertilizers, only evidence shows they are much healthier and better for your garden in the long run, even if they do require more patience.
So many choices for what to feed your plants! What are they exactly, and what tin they accomplish?
Synthetic or Chemical
May exist fabricated up of nitrates, sulfates, phosphates, or other manmade constituents to provide nutrition. These come in powdered, granular, or liquid forms to exist sprayed, and can have negative environmental impacts.
Organic
Created with plant or animal byproducts like fish, os, claret meal, manure, and others. May come in powdered, granular, liquid spray, or bulk "raw" forms. Gentler on the surroundings, though slower acting.
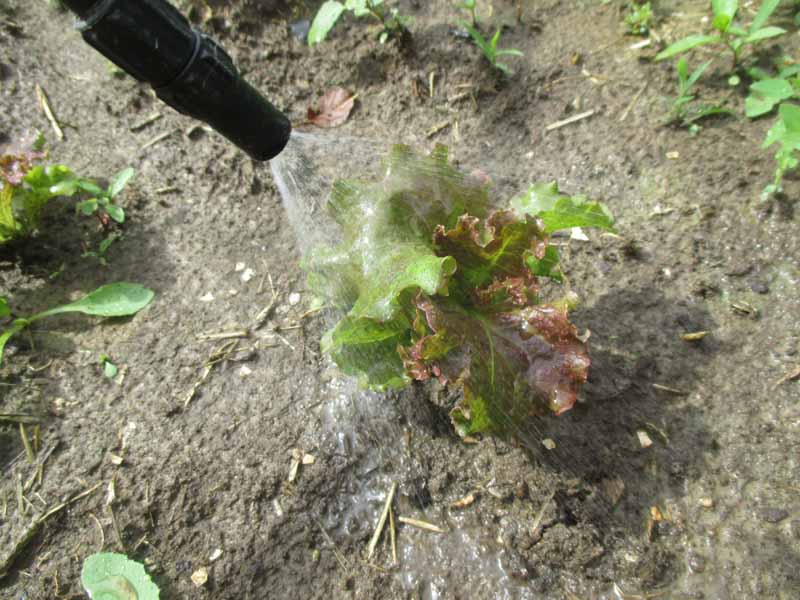

Natural Amendments
These may include compost, mulch, worm castings, wood ash, lime, and other more often than not natural additions that heighten nutrient utilise and availability. These don't have a designated Northward-P-K amount, sometimes non even containing whatsoever of these three nutrients at all.
There are also some popular synthetic/chemical choices:
- Sodium nitrates – A nitrogen fertilizer, though under scrutiny for possible negative wellness and environmental effects.
- Phosphates – Provides phosphorus, but can leach into the environment, rivers, and the ocean.
- Ammonium sulfates – Either ammonium sulfate, nitrate, or chloride, each is responsible for releasing large amounts of nitrogen for free use.
- Urea – Provides nitrogen and poses equally a depression-cost fertilizer.
Chemical fertilizers are very appealing to the mainstream, especially for commercial growers and farmers.
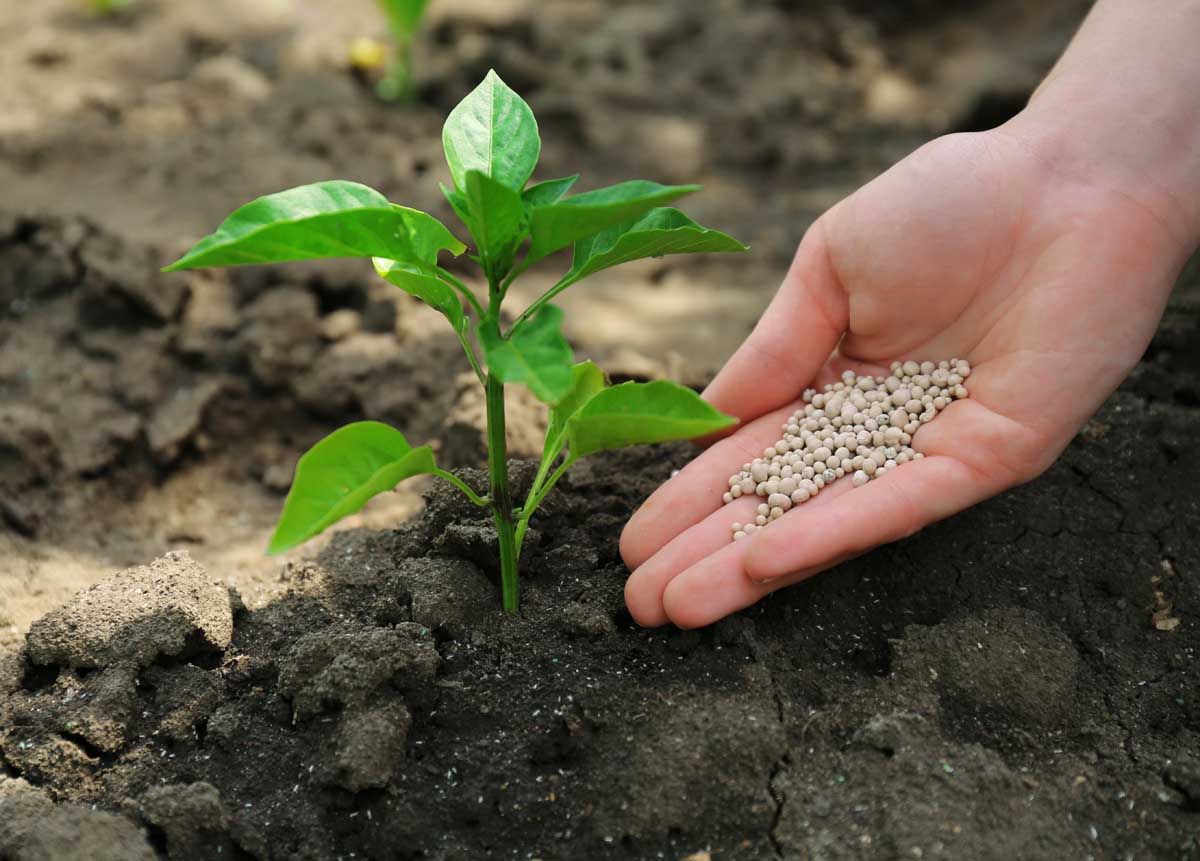

Even so, at that place is increasing controversy – peculiarly in modern times – near the health effects and environmental impact of these chemicals, documented closely by the EPA (U.S. Ecology Protection Agency).
Nitrates and phosphates contribute to runoff and ecological damage, while the consumption of foods and water with vestiges of sodium nitrates and other chemicals are suspected of being potentially unsafe.

Espoma Organic Bone Meal via Abode Depot
As a effect, organic methods of gardening are becoming quite popular, and are considered wholly safe and guilt-free. Turn to these options for a chemic-complimentary environment and make clean nutrient:
- Fish emulsion – Typically a byproduct from fisheries, this provides an organic N-P-Grand ratio, tending to be higher in nitrogen than P or G.
- Bone meal – Another byproduct, this gives greater amounts of phosphorus and nitrogen – especially helpful for bulb, root, and transplant development.
- Blood repast – This byproduct boasts high levels of nitrogen, and comes in stale or powdered form.
- Manure or guano – Fertilizers of this type are sourced from many animals including chickens, rabbits, sheep, cattle, horses, pigs, and even seabirds, worms, or bats.
- Biofertilizers – These are made of soil bacteria that boost natural production of nutrients in the soil around roots, particularly nitrogen, through the process of nitrogen fixation.
- Cover crops – Bachelor as purchasable seed, these are temporarily cultivated to boost presence of soil bacteria for nearby plants, or to act as green manure and increasing nutrient levels, bioavailability, and soil health overall.
Likewise commercial fertilizers, whether organic or inorganic, you can turn to some other natural amendments, not only to provide nutrition, simply to ramp up availability of nutrients in other ways.
Compost
Yous tin create your ain compost from waste materials at home, or purchase commercially or publicly made compost from garden centers or city landfills.
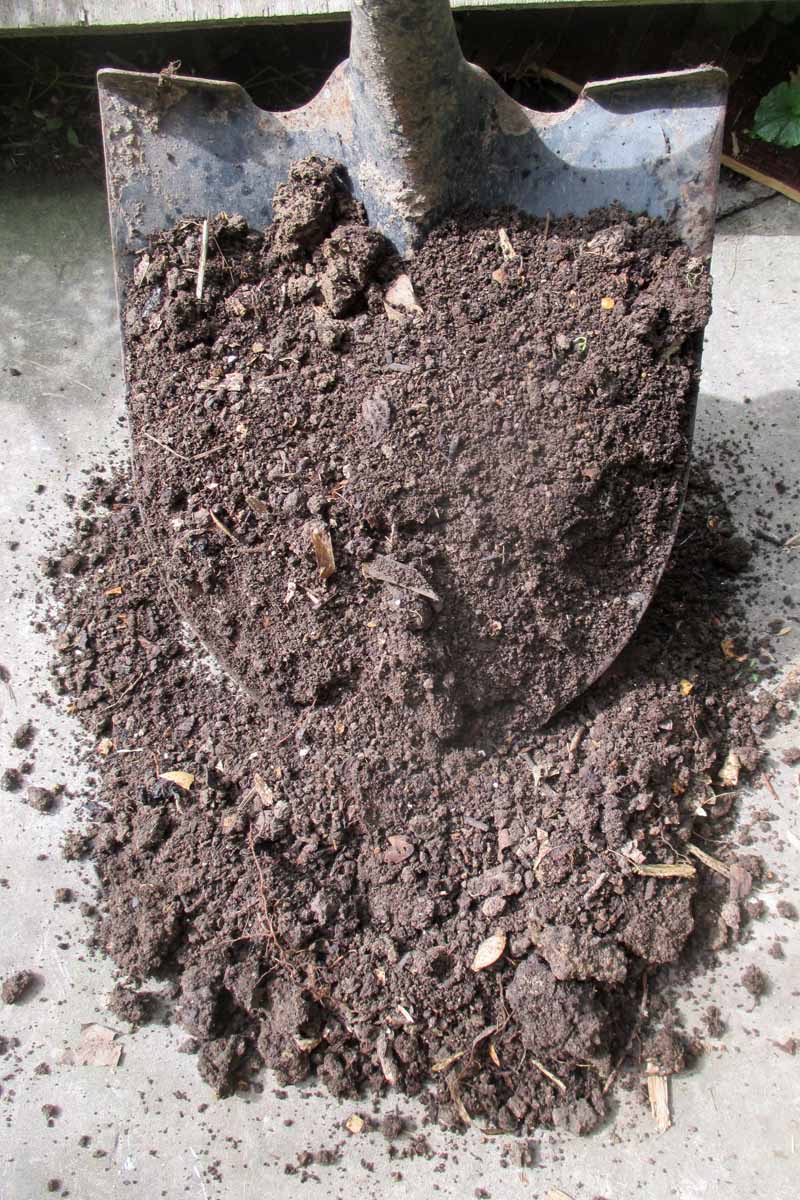

While you may pre-improve beds or side-dress veggies, shrubs, or flowers with compost at times as a plant food, thinking of compost as a fertilizer (like any of the products from the previous section) is actually not the best practice, co-ordinate to reliable sources.
Rather, i must retrieve nearly compost as a food with a small-scale amount of many nutrients, yes – simply more so as having a capacity to increase the soil itself equally a nutrient-friendly medium.

Blackness Kow Composted Cow Manure via Abode Depot
Farther, the addition of composted organic affair revs up microbial activity in the soil, increasing nutrient output in large amounts, though much more slowly than fertilizers.
Here are some tips on using compost for boosting nutrients in your garden:
1. Add Merely Completely Finished Compost
Sometimes, this means waiting for all nitrogenous materials to fully break down. The time for this varies depending on what ingredients are added – if compost is too fresh or "hot," it may burn and impairment plants rather than helping.

two. Add together the Right Amount
Too much can overstimulate the microbial presence in the soil, causing an overproduction of nutrients that damages growth and health.
A good style to know how much to add is to measure the surface expanse of your bed and calculate how much to add weight-wise in gild to spread a 1-inch-thick layer of compost over the entire area.
3. Compost Materials that Are Nutrient-rich
Adding sure natural materials ensures that food levels are optimal. Assistant peels boost potassium, for example, while eggshells increase the calcium.
Avoid adding harmful chemicals and unnatural materials, besides as relying on but one material. Give diverseness for more nutrients!
Mulch
Fresh organic matter added at the bases of plants – or in between rows – gives a piffling actress nutrition in the form of green manure. Information technology also helps with keeping weeds downwards, maintaining moisture, and forestalling erosion and runoff.
Some great examples are:
- Dead leaves
- Hay
- Harbinger
- Grass clippings
- Newspaper (untreated)
- Cardboard (untreated)
- Shredded leaves
- Pine needles (just for utilise around copse, shrubs, and berries)
Like to compost, mulch shouldn't be thought of as a fertilizer that brings oodles of nutrients.
Instead, it is more than of a medium-enhancer for soil: boosting the ability of nutrients to be absorbed, particularly by upping carbon amounts. Carbon then catalyzes nitrogen breakdown, making this important nutrient bachelor more than rapidly.

Like compost, mulch comes with a caveat: too much, and the nitrogen in the soil can be rendered useless. Exist modest with your mulch!
Too fertilizer, compost, and mulch, in that location are a handful of other natural amendments you can use to jazz up your soil microbiome and food availability.
Read more about mulching techniques here.
Wood Ash
In advisedly calculated amounts, ash ups levels of potassium in the soil naturally, and can make it more than alkaline.
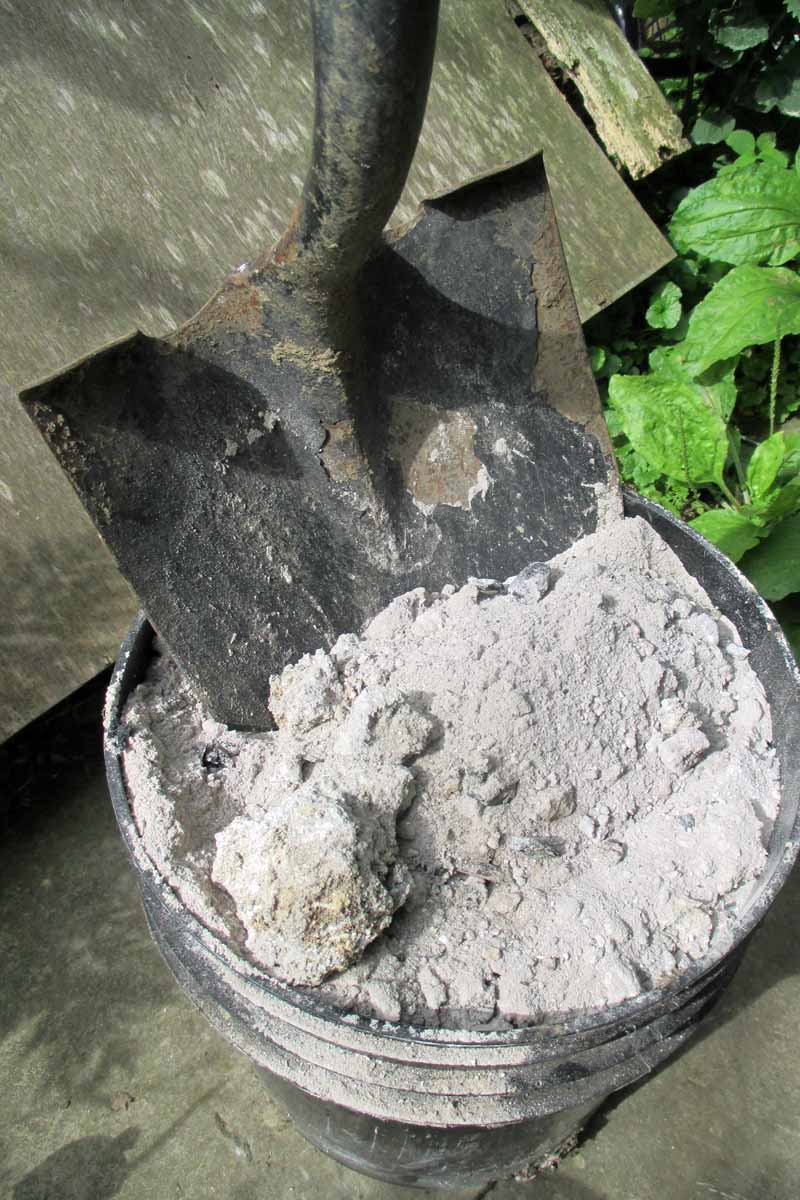

Non recommended for plants that prefer acid soils or those already loftier in pH and potassium, Mother World News recommends that no more than 25 pounds of wood ash be used on 1,000 square feet of space per twelvemonth.
You can learn more most how to use wood ash in the garden in this guide.
Lime
Garden lime boosts nutrients and tweaks the pH of soil, though it'southward best for use merely when magnesium is missing.

Jobe'southward Organics Garden Lime via Amazon
Dolomitic lime has college magnesium levels, while the calcific type boasts more calcium. Both tin raise pH, so avoid applying in already alkaline soils or about plants preferring acidity.
Lean more virtually using garden lime here.
Gypsum
Gypsum adds a calcium boost and helps to break up high dirt, compact, and hard-pan soils. It reduces salt and sodium levels also. For smaller areas, you can employ 'Down to Earth' organic garden gypsum which is available in 5lb containers.

Downward to Earth Organic Garden Gypsum via Amazon
For larger a larger area, you can pick up this 36lb bag from Espoma.
Gypsum is not recommended for frequent use, though it works great for fresh broken basis. It is pH neutral, merely known to slightly acidify.
As you lot have read and so far, there is a huge assortment of institute foods out there, each doing dissimilar things, and providing varying nutrients and actions in your garden.
With and then many nutrients and amendments, what exactly can you accomplish – or even fix – with them?
More specifically, how, when, and why should you employ them? Permit'due south have a look!
A Fourth dimension and Place for Nutrients
It's like shooting fish in a barrel to think that you tin't take too many nutrients.
Choosing between adding the Correct nutrient and only dumping on a lot of everything is like the difference between night and day.
Make sure to accept note of the important insights and tips ahead before selecting what plant nutrients you lot need.
Routinely adding tons of compost, mulch, fertilizer, and other amendments in plentiful amounts tin't be bad, right?
Wrong!
Skilled farmers and gardeners know that there is a correct fourth dimension and setting for adding specific nutrients to bring plant and soil health dorsum into residual.
To get acquainted with this subtle art, they acquire what signs, symptoms, pests, diseases, soil states, and even stages of growth in a plant's life to wait for earlier deciding what nutrients to add.
Choosing betwixt adding the RIGHT nutrient and just dumping on a lot of everything is like the difference betwixt night and day. Make sure to take note of the important insights and tips ahead before selecting what plant nutrients you need.
Advent and Color
A lack or imbalance of nutrients can exist determined according to a few universal, adequately easy-to-interpret signs and symptoms.
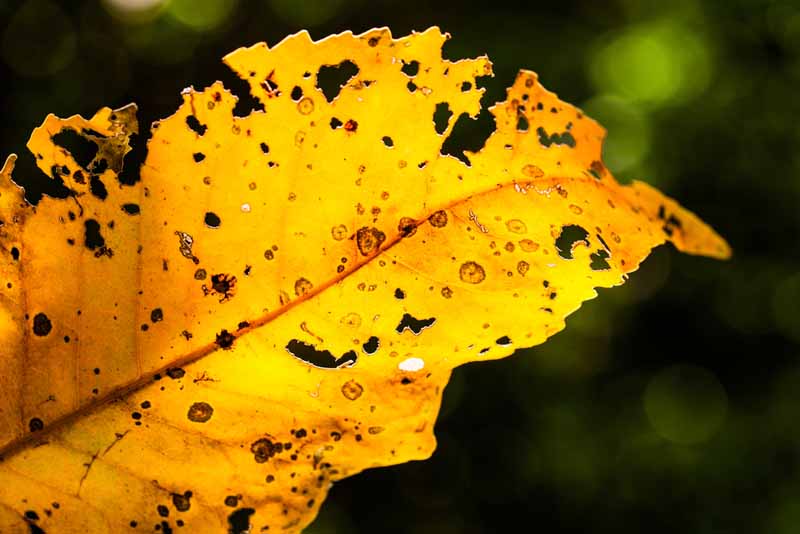

However, practise have intendance to know exactly what healthy plants should look like before reading into any abnormal appearances! The following are fantabulous symptoms to use in looking for certain nutrient deficiencies, provided past the Arizona University Cooperative Extension.
- Yellowed leaves (old growth) – Indicates a nitrogen deficiency.
- Yellow-edged leaves (old growth) – Indicates a magnesium deficiency.
- Warped, misshaped new leaves – Reveals a calcium deficiency.
- Majestic/scarlet leaves – Lack of phosphorus.
- Deformed fruits – Typically due to potassium, though nitrogen excess can contribute.
- Bloom finish rot (tomatoes) – Widespread cause is from lack of calcium.
- No flowering/dropped flowers – Can signal to lack of phosphorus.
- Light dark-green leafage (rather than nighttime green) – An "anemic" appearance could be nitrogen deficiency.
- "Burnt" foliage-tip advent – Points to depletion of phosphorus.
- Abnormally dark green old foliage – Another sign of not plenty phosphorus.
- Dark black or scorched leaf appearance – Potassium deficiency.
- Wilted onetime growth – Potassium deficiency.
Plant Growth Stages
As well studying abnormal appearances, you can acquire whether or non to give specific nutrients to a institute depending on what stage of growth it is in, and even what diversity or species of institute information technology is.
Immature Growth
Nitrogen is peculiarly helpful to give, though adequate levels of all nutrients are disquisitional at this phase.
Newly Transplanted
Will do good specially from higher amounts of root-supporting nutrients, similar phosphorus and potassium.
Blossoming
Benefits from phosphorus, potassium, and calcium in detail.
Fruiting
It's of import to include decent amounts of phosphorus and potassium, while not overdoing it with nitrogen.
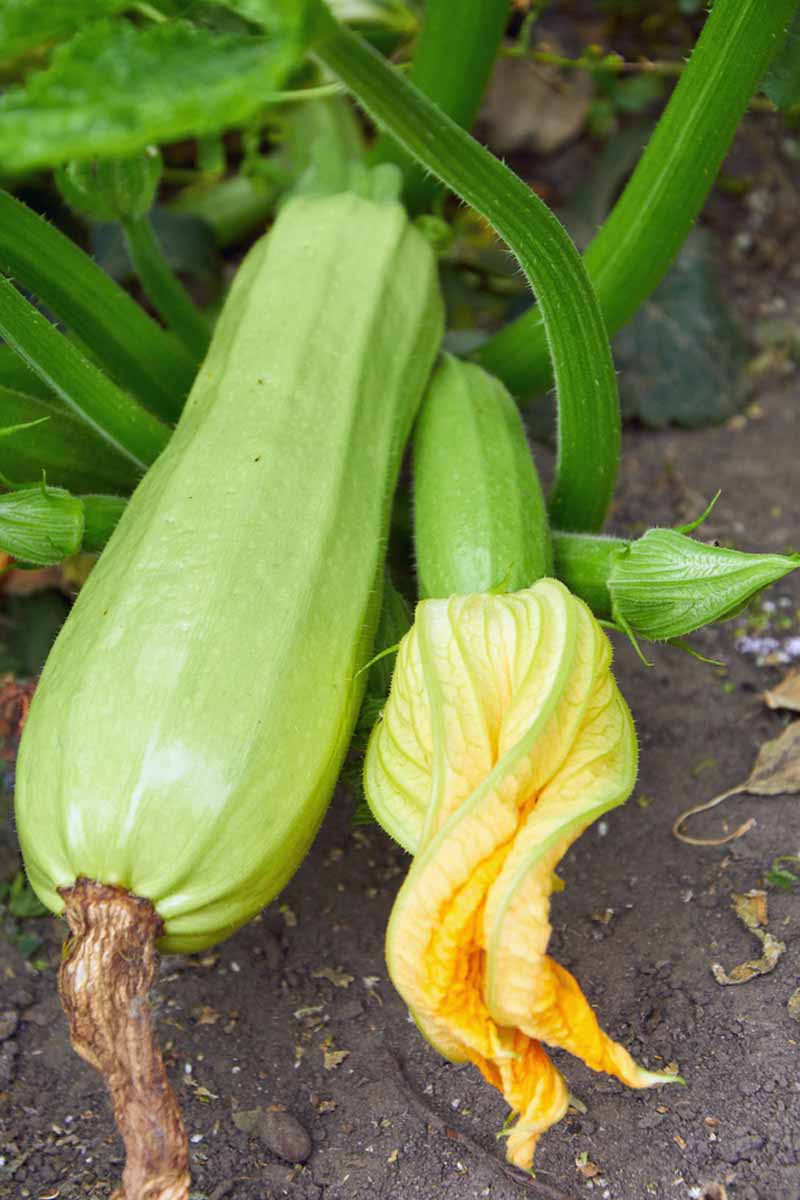

Here are some specific plant species and nutrients that are of import for their proper growth and evolution:
- Garlic – Benefits from phosphorus and potassium for good bulb and root development.
- Lettuce – Flourishes with adequate nitrogen and magnesium levels for good for you, bonny greens.
- Roses – Some boosts of phosphorus could aid with stronger, healthier blooms.
- Carrots – Roots grow stronger and tastier with adequate phosphorus and potassium.
- Tulips – A loftier phosphorus and potassium fertilizer supports peachy bulb growth.
- Squash – Acceptable phosphorus, calcium, and potassium protect against flower failure and promote healthy fruiting.
- Tomatoes – Need nitrogen for stiff vine growth, phosphorus for good blooms, and potassium and calcium for strong, healthy fruits.
Using Nutrients to Preclude Found Problems
In some cases, plants suffer from certain illnesses – fungal, viral, bacterial, and more than – due to a lack of sure nutrients in their environment.

Every bit with people, the intake of certain nutrients tin be a key to forestalling disease, similar vitamin C's associations with reducing symptoms of the mutual common cold.
How does this happen with plants? Let'due south take a await.
Fungal Constitute Diseases
Downy mildew, fusarium, and others directly invade establish tissues that are weak from a lack of nutrients. A rise in fungal illness may signify the need for calcium, potassium, or phosphorus.
Viral Plant Diseases
Excess of certain nutrients (especially nitrogen and phosphorus) can increment susceptibility to viruses. This tin sometimes exist counterbalanced with more than potassium.
Bacterial Constitute Diseases
After adding whatsoever amendment, wait a week or two and spotter for comeback. If it'due south not obvious that your plants are getting healthier, then y'all may want to diagnose for other problems merely to exist safe.
Depression calcium, nitrogen, and potassium can make your plants susceptible to bacterial illnesses, equally described by the University of Florida Extension. On the other hand, too much nitrogen tin help sure bacteria to thrive as well.
If you run across any of the to a higher place categories of disease, effort balancing the nutrients in your soil by post-obit each respective proffer.
After adding any amendment, expect a week or two and picket for improvement. If it'due south not obvious that your plants are getting healthier, then you may want to diagnose for other problems just to exist condom.
If plants fail to recover, take it as a sign that they are too diseased and unhealthy to improve – and remove them from your garden quickly if that is the case.
Pests
A lack of proper plant nutrition can have a big impact on the influence of pests.
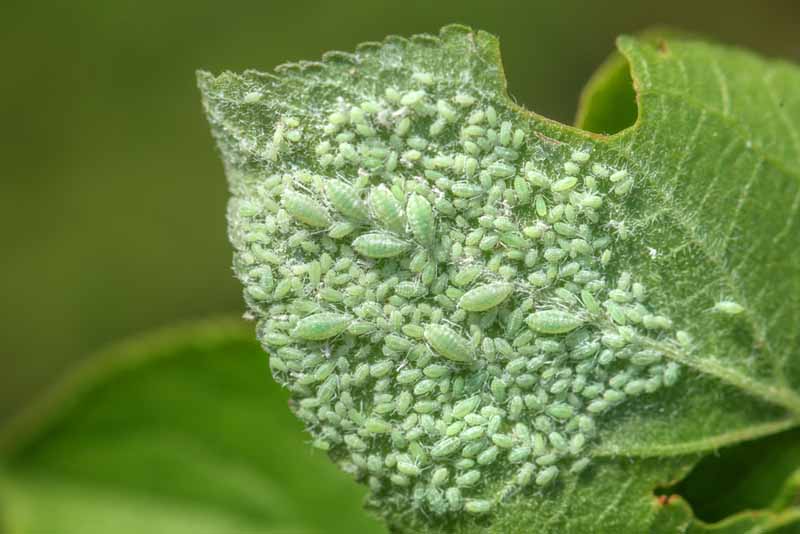

Information technology'due south a no-brainer that a nutrient-depleted, unhealthy field volition be much more vulnerable to pests, in comparing to a perfectly nutrient-salubrious field – equally studied and tested in this article from Ag-USA.net.
Some nutrient factors in the soil may contribute to the increased likelihood of undesired pest outbreaks. Excessive nitrogen is the most notable: studies cited past eXtension.org reveal that too much leads to increased pest populations of arthropods (i.due east. aphids, mites, etc.), so have care not to get overboard!
Weak, undernourished plants also transport out chemic signals to pests that they are languishing – thus, depleted plants without acceptable diet quickly hasten their own cease.
On the other hand, healthy plants with enough of nutrients do merely the reverse, attracting more benign bugs than harmful varieties, even some that are fix to dine on nearby pests to prevent impairment!
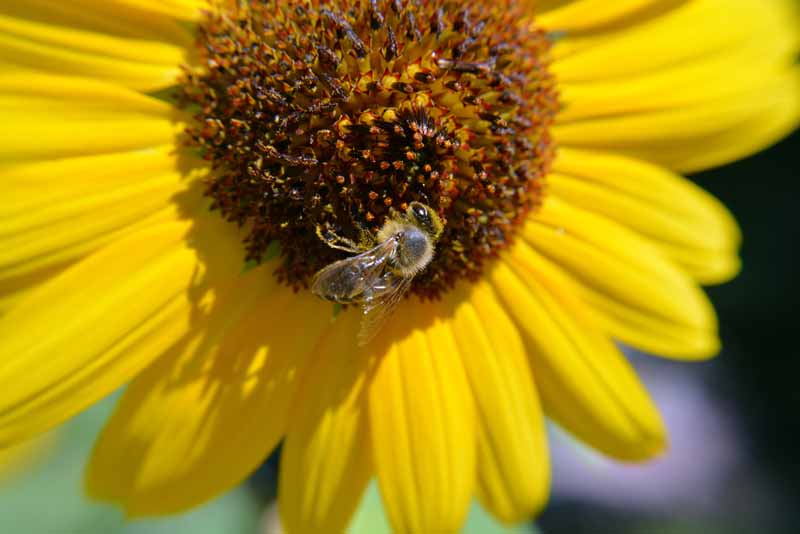

For that reason, providing a full range of nutrients for your plants is the all-time way to forestall pests every bit organically equally possible.
Amendments Tin can Impact Soil Weather condition
Plant nutrients tin agree sway over soil conditions at times, nigh specifically on soil pH, or acidity versus alkalinity. In fact, it tin be better said that pH determines nutrient availability, rather than the other way around!
More acidic soils tend to take less bioavailability of certain nutrients, such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, and others; alkaline soils may accept an excess of the aforementioned. Either way, an extreme on either side of the spectrum is not ideal for most plants.
To some degree, adding certain amendments and nutrients tin aid correct pH imbalances, though non always. Adding loftier-K fertilizers, lime, and wood ash, for case, may bring pH up to a more alkaline level, or neutralize acidic soils.

On the other mitt, gypsum tends to brand soil more acidic (though not always), with their high calcium and magnesium levels.
Very high nitrogen applications (especially ammonia-based ones) sometimes set off an acrid-creating chain reaction in the soil, which is successful, but non always environmentally friendly, due to the output of nitrates.
What's the bottom-line best way to meliorate pH?
Amend beds with healthy, adequate amounts of natural, microbe-rich compost in between plantings. In that location is no better way to naturally modulate pH than to leave the work to the soil microbiome, which knows how to attenuate pH organically on its own.
Nutrients – A Necessity
What would gardening be without the use and mastery of nutrients? Pretty bleak, if you ask me!
Whether you're dealing with plant sickness, pests, or simply wanting the all-time blooms or fruits on the cake, get acquainted with all the different amendments and fertilizers out at that place for those awesome results.
In fact, using them is completely necessary, an accented requirement in a adept number of instances.

I hope this article prepares you with the best starting cognition out there – the ideal N-P-Thou numbers for your needs, what exact subpoena is your best bet in any given state of affairs, and fifty-fifty comparisons between the benefits of organic versus inorganic fertilizers.
Even better, knowing all the unlike ways to diagnose a plant's specific needs lets you but look at a plant and know what food it'due south missing! There'due south no better style to have the healthiest and most beautiful plants, am I right?
Accept anything to share about your knowledge of plant nutrients? Whatever comments or questions on what you accept learned here? Ask abroad! Talk to u.s.a. below in the comments section.
Happy gardening!
If you lot enjoyed this article, take a wait at some our other gardening guides such equally:
- What Every Gardener Should Know about Peat Moss (Plus 5 Alternatives)
- Succession Planting: How to Grow Crops for a Continual Harvest
- Growing Borage as a Cover Ingather and for Green Manure
shrefflerdozziess.blogspot.com
Source: https://gardenerspath.com/how-to/composting/plant-nutrients/
Postar um comentário for "what native plant is taking over parts of the everglades due to excess nutrients"